「二部グラフの最大安定集合問題」について知っていれば典型問題ですね。
問題概要
のグリッドがあります。各マスは白黒に塗られています。今、白いマスにできるだけ多くのコマを置きたいものとします。
- 各マスに 1 個のみコマを置ける
- コマを置けるのは白いマスのみである
- 隣り合う白マスの双方にコマを置くのは禁止である
という制約下で最大何個のコマを置けるかを求めてください。
制約
最大安定集合問題
まずそもそもこの問題は、「グラフの最大安定集合問題」そのものの形をしています。最大安定集合問題とは、下図のように「頂点のなかから、どの 2 頂点も辺で結ばれていないようにいくつかの頂点を選ぶとき、その最大個数を求める」という問題です。

一般のグラフでは最大安定集合問題は NP-hard であり、多項式時間ではおそらく解けないと考えられています。しかしながら二部グラフであれば、最大安定集合問題は、二部マッチングに帰着して解けることが知られています。その詳細については、次の記事に記しています。
グリッドグラフは二部グラフ
二部グラフとは、各頂点を「赤色」と「青色」に塗り分ける方法であって、「白色頂点同士が隣接することはなく黒色頂点同士が隣接することはない」という条件を満たす方法が存在するようなグラフのことです。
今回のようなグリッドグラフは、下図のように市松模様になるように、各マスを赤色と青色に塗り分けることができます。
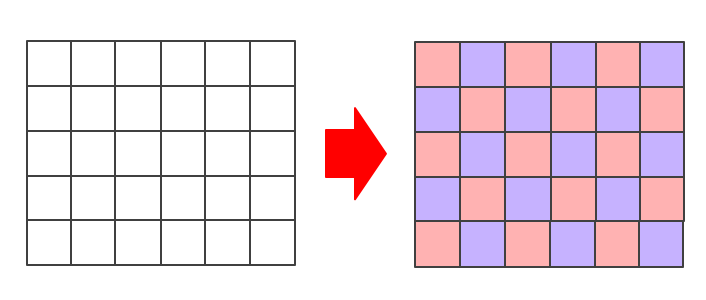
今回のグラフは、グリッド全体が頂点集合となるのではなく、黒色マスを除いた白色マスのみが頂点集合となります。しかしそれでも、グリッド全体が二部グラフですので、「グリッドグラフの部分グラフ」も二部グラフとなります。
まとめますと今回の問題は、「二部グラフの最大安定集合問題」へと帰着されました。二部グラフの最大安定集合問題の答えは、実は、二部グラフの最大マッチングの値に一致します。よって、Ford-Fulkerson 法などの最大流アルゴリズムで解くことができます。
コード
ここでは、高速な二部マッチングアルゴリズムとして、Hopcroft-Karp 法を用いました。
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; struct HopcroftKarp { int sizeL, sizeR; vector<vector<int> > list; // left to right // result vector<bool> seen, matched; vector<int> level, matching; // base HopcroftKarp(int l, int r) : sizeL(l), sizeR(r), list(l, vector<int>()) { } inline vector<int>& operator [] (int i) { return list[i]; } inline void addedge(int from, int to) { list[from].push_back(to); } inline friend ostream& operator << (ostream& s, const HopcroftKarp& G) { s << endl; for (int i = 0; i < G.list.size(); ++i) { s << i << " : "; for (int j = 0; j < G.list[i].size(); ++j) { s << G.list[i][j]; if (j + 1 != G.list[i].size()) s << ", "; } s << endl; } return s; } // methods void hobfs() { queue<int> que; for (int left = 0; left < sizeL; ++left) { level[left] = -1; if (!matched[left]) { que.push(left); level[left] = 0; } } level[sizeL] = sizeL; while (!que.empty()) { int left = que.front(); que.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < list[left].size(); ++i) { int right = list[left][i]; int next = matching[right]; if (level[next] == -1) { level[next] = level[left] + 1; que.push(next); } } } } bool hodfs(int left) { if (left == sizeL) return true; if (seen[left]) return false; seen[left] = true; for (int i = 0; i < list[left].size(); ++i) { int right = list[left][i]; int next = matching[right]; if (level[next] > level[left] && hodfs(next)) { matching[right] = left; return true; } } return false; } int solve() { seen.assign(sizeL, false); matched.assign(sizeL, false); level.assign(sizeL+1, -1); matching.assign(sizeR, sizeL); int res = 0; while (true) { hobfs(); seen.assign(sizeL, false); bool finished = true; for (int left = 0; left < sizeL; ++left) { if (!matched[left] && hodfs(left)) { matched[left] = true; ++res; finished = false; } } if (finished) break; } return res; } }; const int dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0}; const int dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; int main() { int R, C; cin >> R >> C; vector<string> fi(R); for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) cin >> fi[i]; HopcroftKarp hk(R*C, R*C); int V = R*C; for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j) { int left = i * C + j; if (fi[i][j] == '*') { --V; continue; } if ( (i + j) % 2 == 1 ) continue; for (int dir = 0; dir < 4; ++dir) { int ni = i + dx[dir], nj = j + dy[dir]; if (ni < 0 || ni >= R || nj < 0 || nj >= C) continue; if (fi[ni][nj] == '*') continue; int right = ni * C + nj; hk.addedge(left, right); } } } auto res = hk.solve(); cout << V - res << endl; }